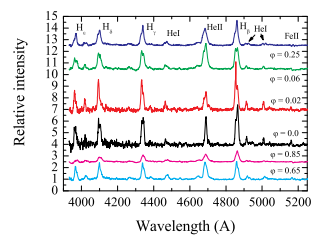
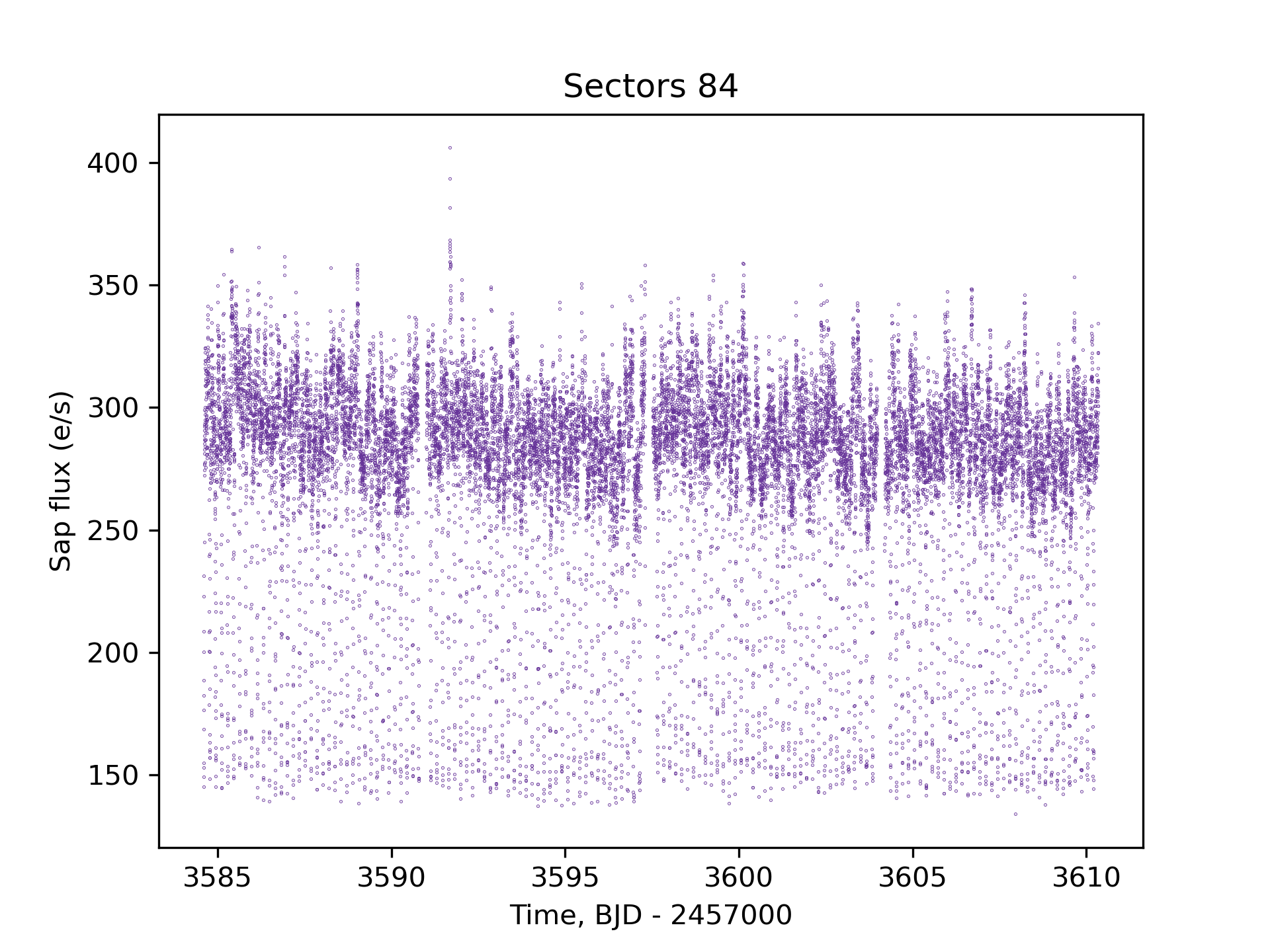
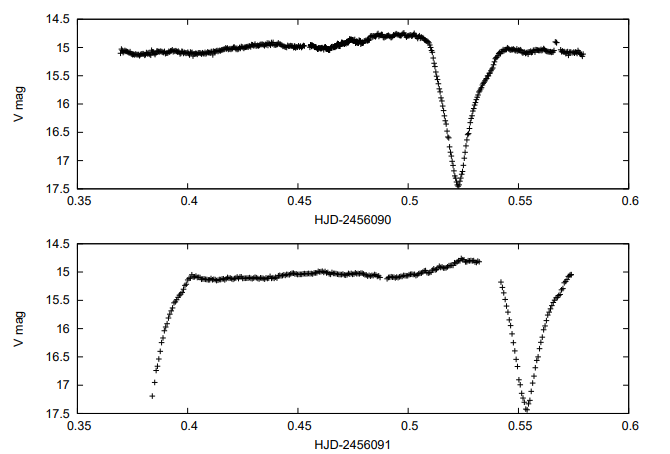
HBHA 4705-03 is a nova-like eclipsing cataclysmic variable star located in the constellation Cygnus. It was initially discovered as a hydrogen emission-line source in the HBHA catalog. The system consists of a white dwarf and a donor star, with mass transfer occurring via an accretion disk. A detailed photometric and spectroscopic study in 2013 revealed that the star exhibits deep V-shaped eclipses and has an orbital period of approximately 4.12 hours. Spectral and photometric features indicate the presence of an accretion disk and a high orbital inclination of around 81.5°. The mass of the white dwarf is estimated to be about 0.54 solar masses, while the donor star has a mass of approximately 0.19 solar masses. HBHA 4705-03 is valuable for studying the structure and behavior of high-inclination cataclysmic variable systems.
Photometry & Images
| Catalogue | Gaia |
| RA | 334.209650768° |
| DEC | 46.778127200° |
| U | -- |
| B | -- |
| V | -- |
| Parallax (mas) | 2.52 ± 0.02 |
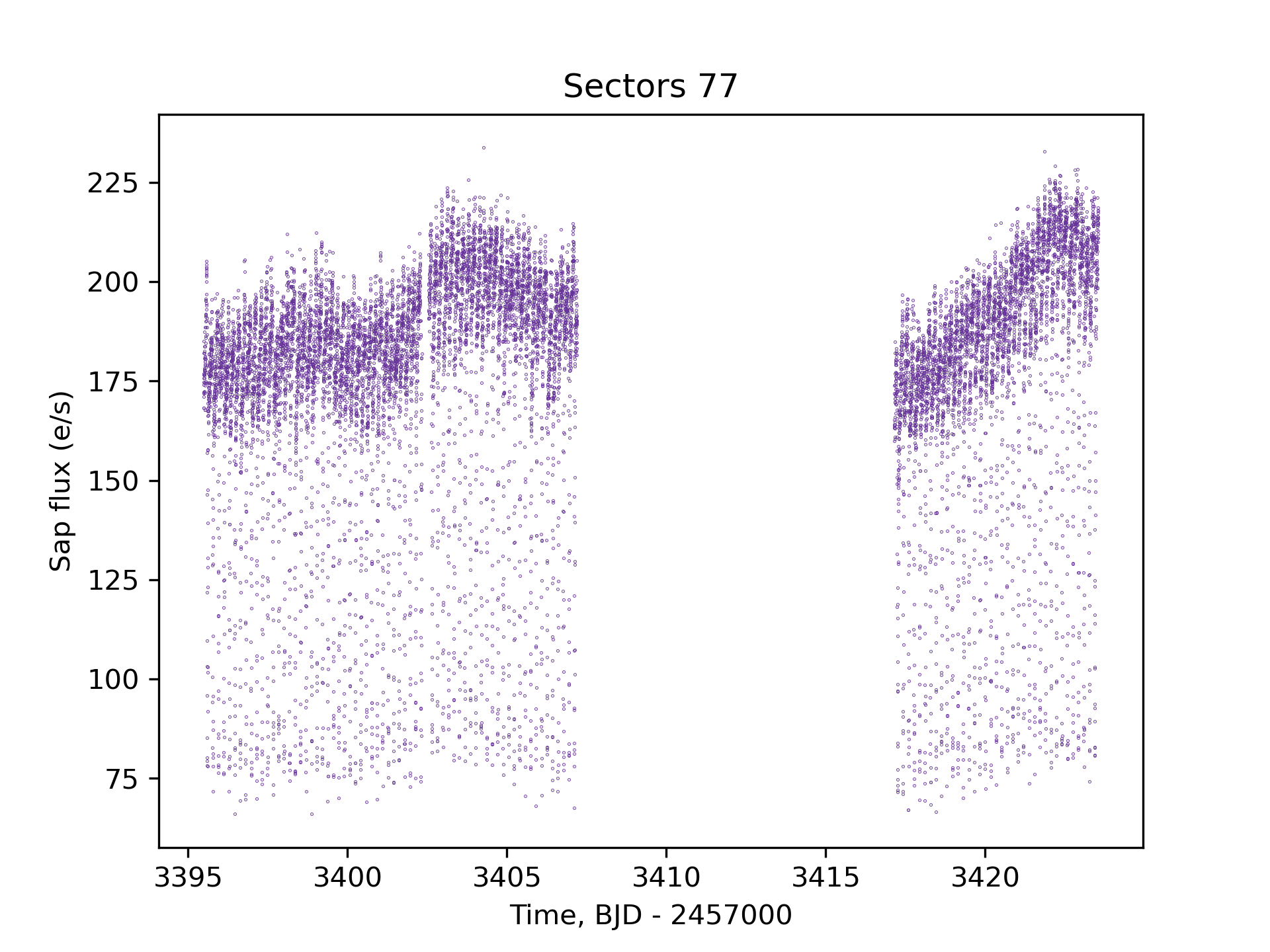
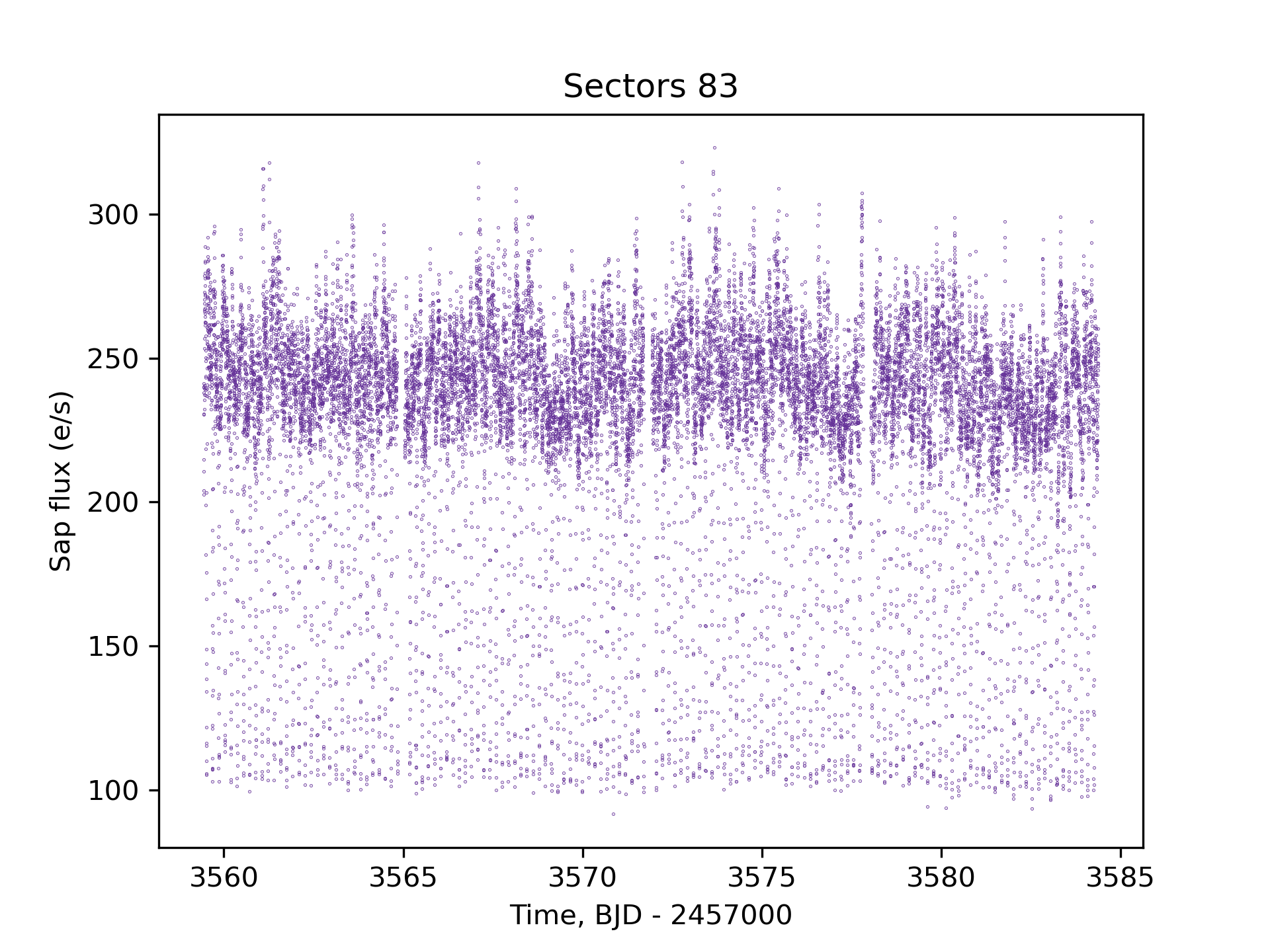
TESS Data
Spectroscopy